PDA (Patent Ductus Arteriosus) Closure
<script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js"></script> <!-- Squarespace --> <ins class="adsbygoogle" style="display:block" data-ad-client="ca-pub-9997413508115323" data-ad-slot="7569173141" data-ad-format="auto" data-full-width-responsive="true"></ins> <script> (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({}); </script>
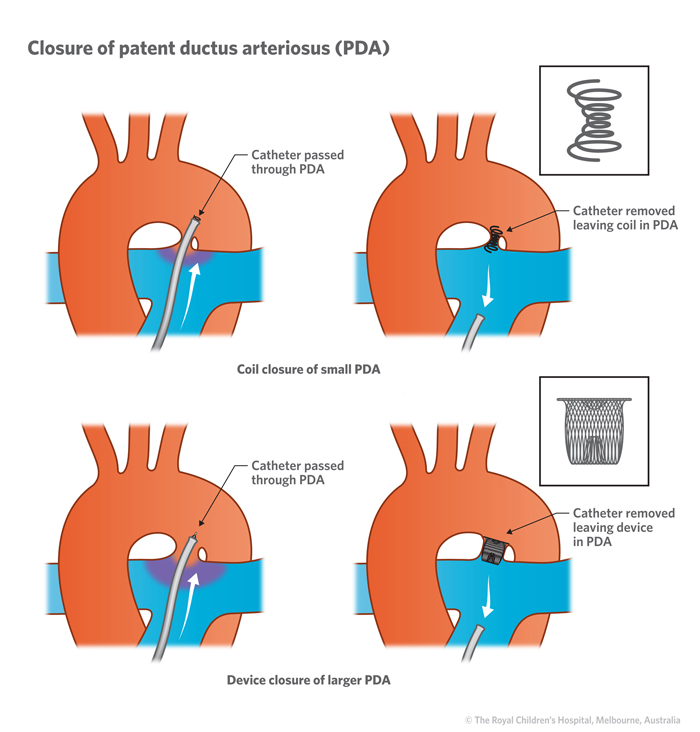
What Is Patent Ductus Arteriosus?
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is an extra blood vessel found in babies before birth and just after birth.
In most babies who have an otherwise normal heart, the PDA will shrink and close on its own in the first few days of life. If it stays open longer, it may cause extra blood to flow to the lungs. Problems are most likely if the PDA is large. Some smaller PDAs that don't close early will seal up on their own by the time the child is a year old.
What Happens in Patent Ductus Arteriosus?
The ductus arteriosus is a normal blood vessel that connects two major arteries — the aorta and the pulmonary artery — that carry blood away from the heart.
The lungs are not used while a fetus is in the womb because the baby gets oxygen directly from the mother's placenta. The ductus arteriosus carries blood away from the lungs and sends it directly to the body. When a newborn breathes and begins to use the lungs, the ductus is no longer needed and usually closes by itself during the first 2 days after birth.
If the ductus doesn't close, the result is a patent (meaning "open") ductus arteriosus. The PDA lets oxygen-rich blood (blood high in oxygen) from the aorta mix with oxygen-poor blood (blood low in oxygen) in the pulmonary artery. As a result, too much blood flows into the lungs, which puts a strain on the heart and increases blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries.
In infants born with other heart problems that decrease blood flow from the heart to the lungs or decrease the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the body, the PDA may actually help, and the doctor might prescribe medicine to keep the ductus arteriosus open.
Under General Anaesthetic
BiPlane views
Equipment:
Barts angiopack
6F femoral sheath (venous)
5F femoral sheath (arterial)
Amplatz Super Stiff J-tip wire 0.035” x 260cm (Dr A Jain/ Dr A Bhan)
5F JR4 diagnostic catheter (for venous sheath)
5F MPA1 diagnostic catheter (for venous sheath)
5F Pigtail catheter (for arterial sheath)
Cook femoral needle
Backstop
PDA plug (ask for size)
PDA delivery system
<script async custom-element="amp-auto-ads" src="https://cdn.ampproject.org/v0/amp-auto-ads-0.1.js"> </script>